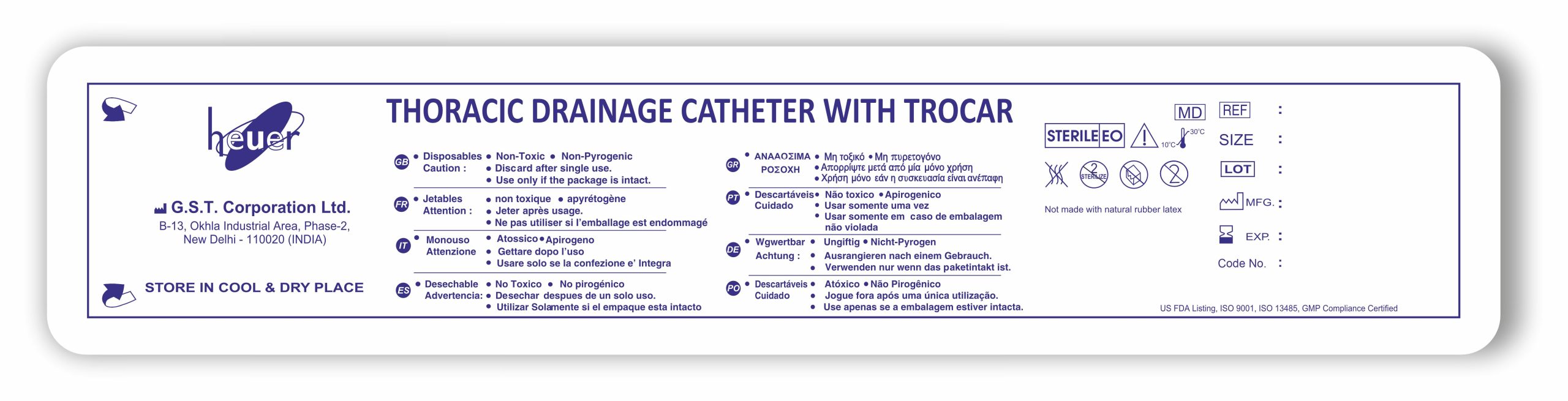
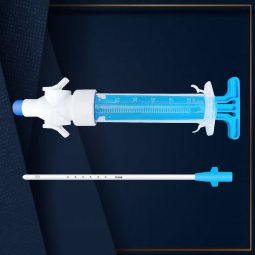
Description
Feature of Thoracic Drainage Catheter
Drainage Holes: Multiple Mini holes or parts let water or air in the tube for venting. These ports are specifically placed to smooth way to drainage out from the lungs.
Connecting Tubing: Thoracic catheter has a connector for drain connection. It collects fluid in room or underwater sealing system as needed.
Placement Marker: Thoracic drainage catheters have non-radiopaque markers visible on x-rays, aiding in confirming lung implantation success and long-term node health monitoring.
Suture Holes or Flanges: It may possible to have suction holes or flanges so that the wires can be safe and securely connect to the skin to prevent leaking.
Stylet or Trocar: For insertion, pierce chest wall with stylet/trocar, guide needle into thoracic cavity. Once positioned, remove stylet, leave flexible catheter.
Thoracic Drainage Catheter Safety & Uses:-
- Pneumothorax: Remove air from pleural space.
- Pleural Effusion: Drain excess fluid.
- Empyema: Remove infected fluid/pus.
- Hemothorax: Drain blood from pleural cavity.
- Post-surgical Drainage: Drain fluid/air post-thoracic surgery.
- Diagnostic Procedures
- Tension Pneumothorax
To safely use a thoracic drainage tube, keep everything sterile, secure the tube properly, regularly check its function, ensure the drainage system works, monitor the patient’s vital signs, prevent infection, educate the patient on care, and be ready to handle any complications quickly.
Why To Choose Us?
- India’s Trusted Leader Medical Disposables : With over 60 years of experience, we are a leading manufacturer and exporter, serving clients in 30+ countries worldwide.
- Unmatched Quality in Thoracic Drainage Catheter : GSTC is a Thoracic Drainage Catheter Manufacturer and it is made from Soft, Frosted and Kink resistant PVC tubing DEHP Free ensuring the highest safety standards for patients.
- Reliable Delivery : We pride ourselves on delivering your order always on time, with consistent quality and reliability.